Table of contents
Open Table of contents
-
- Explain the term - User Research
- User Research Techniques
- Explaining the term - Requirements Capture Workshops
- Know about - Contextual Interview
- What is Usability Testing
- Prepare the Design or Product to test
- Find your participants
- Write a test Plan
- Take on the Role of Moderator
- Present your findings
- Stakeholder Interview
- Benchmarking
- Expert Review
- Global and Cross-Cultural Research Techniques
- Power Distance (PDI)
- Individualism VS Collectivist
- Uncertainty Avoidance (UAI)
- Long-Term versus Short-Term Orientation (LTO)
- Some Other Research Methods
Explain the term - User Research
- User research is often the first step of a UX design process. One cannot start designing a product or service before understanding what the users want.
- Once it is known, the best practices in user research, it will help to gain first-hand knowledge of the users to design an optimal product— the one that sells better than your competitors’.
- Effective user research helps uncover user pain points, informs design decisions, reduces the risk of creating products that don’t meet user needs, and ultimately leads to the development of products that provide a superior user experience.
- It is an ongoing and iterative process that should be integrated throughout the design and development lifecycle.
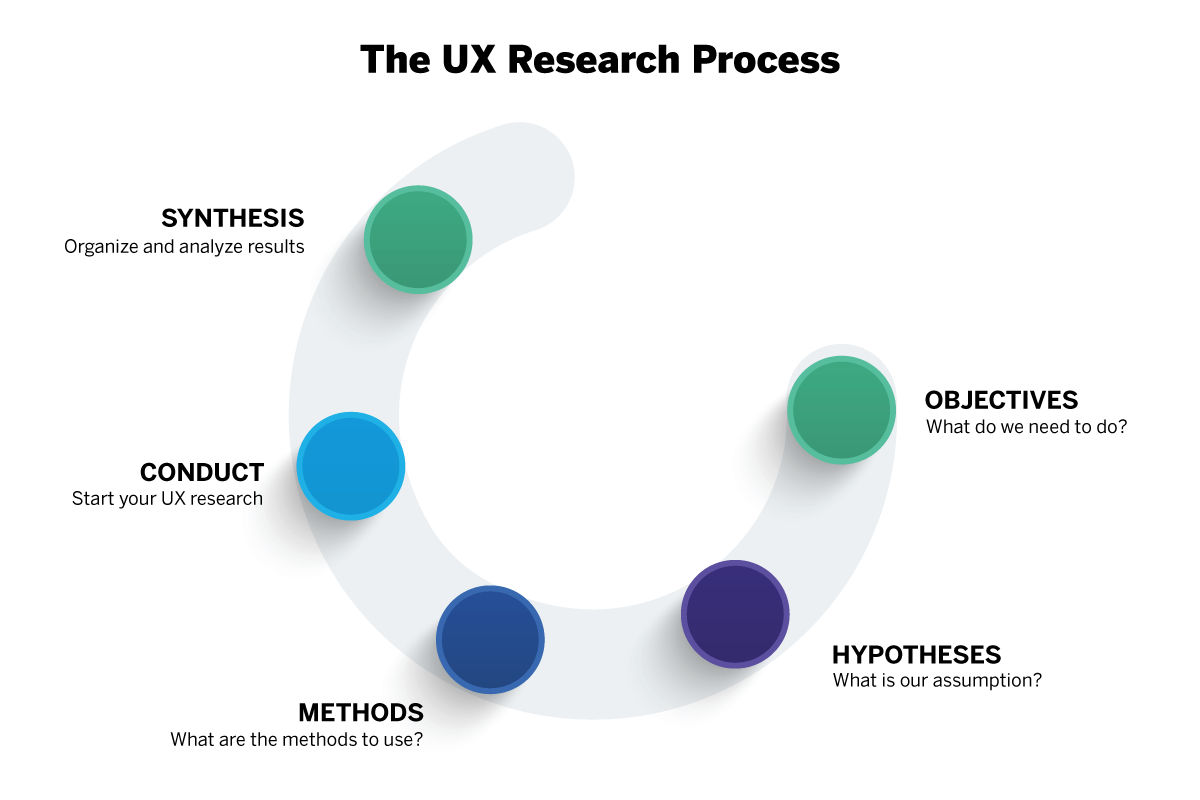
User Research Techniques
User research techniques encompass a wide range of methods and approaches used to gather insights and data about users, their behaviors, needs, and preferences. These techniques are crucial in informing the design and development of user-centered digital products.
This can be conducted without users. However, owing to budget and timescale constraints, it is quite common for service organizations to perform user research without involving users. The following techniques are adopted:
-
With Users
- Requirements Capture Workshops
- Contextual Interview
- Usability Testing
-
Without Users
- Stakeholder Interview
- First-click Testing
- Benchmarking
- Expert Review
Explaining the term - Requirements Capture Workshops
- Requirements capture workshops are a user research method that involves collaborative sessions with key stakeholders, including designers, developers, product managers, and end-users, to gather and define project requirements.
- These workshops are a valuable technique for aligning project goals, understanding user needs, and creating a shared vision for the product.
- Requirements gathering is an important step before commencing with the design. Prioritizing needs and wants is key here.
Steps to be followed :
1. Gather data from users: Do not restrict the definition of users to the actual users of the product. Instead, widen the scope to include a sample that represents each stakeholder.
2. Analyze data to understand user needs: Use statistical techniques to optimize the data into manageable chunks. This will make it easier to analyze and derive insights.
3. Convert user needs into requirements: Once the steps mentioned is completed, it is pretty straightforward to elicit requirements from the hierarchical task analysis. One can then make a list of functional and non-functional requirements.
4. Prioritization: Collaboratively prioritize the ideas and requirements generated during ideation sessions. This helps identify which features or improvements should be given the highest priority.
5. Documentation: Document all requirements, ideas, and decisions made during the workshop. This documentation will serve as a reference throughout the project. Capture requirements in a format that is easy to manage, such as user stories, use cases, or feature descriptions.
5. Follow-Up: After the workshop, share the workshop outcomes and documentation with all participants for validation and feedback. Continue to involve stakeholders and end-users in the development process through regular updates and feedback sessions.
6. Iterate: As the project progresses, revisit and update the requirements as needed. User research is an ongoing process, and new insights may emerge.
Know about - Contextual Interview
- A contextual interview is a user research method that involves conducting interviews with users in their natural environment or within the context of their tasks or activities.
- This approach aims to gain deep insights into how users interact with a product or system in real-life situations, uncovering their needs, pain points, and behaviors within their specific context.
- In a contextual interview, one can observe and listen as the user works. One doesn’t usually offer the tasks or scenarios.
- Contextual interviews are valuable for uncovering user needs and behaviors in authentic settings.
- They provide rich qualitative data that can inform the design and development of products and services, ensuring they are truly user-centered and aligned with users’ real-world experiences.
What is Usability Testing
- Usability testing is a user research method used in the field of UX (User Experience) design to evaluate the effectiveness and user-friendliness of a digital product or interface.
- This method involves observing and collecting feedback from real users as they interact with a prototype, a beta version of the product, or the live product itself.
- The primary goal of usability testing is to identify usability issues, understand user behavior, and gather insights for improving the user experience.
Irrespective of how it carries out the testing, one will need to go through these five phases with Users:
1. Prepare your product or design to test
2. Find your participants
3. Write a test plan
4. Take on the role of moderator
5. Present your findings
Prepare the Design or Product to test
- Before conducting usability testing or any user research, it’s essential to prepare the design or product you want to evaluate.
- Adequate preparation ensures that the testing process goes smoothly and that one can effectively gather insights about the user experience.
- By thoroughly preparing the design or product and the usability testing process, one can maximize the effectiveness of the research and gather valuable insights to inform design decisions and improve the user experience.
- For initial design ideas, One can use a paper ‘prototype’ from pencil sketches or design it through software such as PowerPoint.
Find your participants
- Finding and recruiting participants for user research is a critical step in the research process.
- The quality of the research and the relevance of the findings depend on selecting the right participants who represent the target audience or user group.
- When recruiting participants, it’s crucial to clearly communicate the purpose of the research, the expected time commitment, any incentives or compensation offered, and how their feedback will be used.
- Ensure that participants understand the nature of the research and give their informed consent to participate.
- Additionally, maintain participant confidentiality and privacy throughout the research process.
Write a test Plan
- A test plan in user research outlines the strategy and procedures for conducting a user research study.
- It serves as a comprehensive document that guides the research process, ensuring that the research objectives are met and that the study is conducted effectively.
- Once the test plan is complete and approved, it becomes a roadmap for conducting the user research study.
- It helps ensure that the research is conducted systematically, that objectives are met, and that the research process is well-documented for future reference.
Take on the Role of Moderator
- The role of a moderator in user research involves guiding participants through research sessions, facilitating discussions, and collecting valuable insights about their experiences and interactions with a product or interface.
- As a moderator, the role is to facilitate a productive and comfortable environment for participants to provide honest feedback and insights.
- Effective moderation is essential for generating valuable user research data that can drive product improvements and enhance the user experience.
Present your findings
- Chalking down themes that is noticed, especially if they’re related to the study’s goals.
- It’s a good idea to talk to observers after each session to get a sense of their main learnings.
- Once the sessions are over, look for more answers to the study’s stated goals, and count how many participants acted differently or made certain types of comments.
- Determine the best way to communicate this information to help stakeholders.
Stakeholder Interview
- Stakeholder interviews are a valuable user research method for ensuring that the project aligns with the needs and goals of all relevant parties.
- By engaging with stakeholders early and regularly, one can mitigate misunderstandings, gather valuable input, and enhance the chances of project success.
- These interviews help ensure alignment between the project’s goals and the needs and expectations of stakeholders.
- These interviews allow to step into the shoes of the interviewees and understand their perspective.
- A useful way to get the business’ input into the project is through a UX Stakeholder interview.
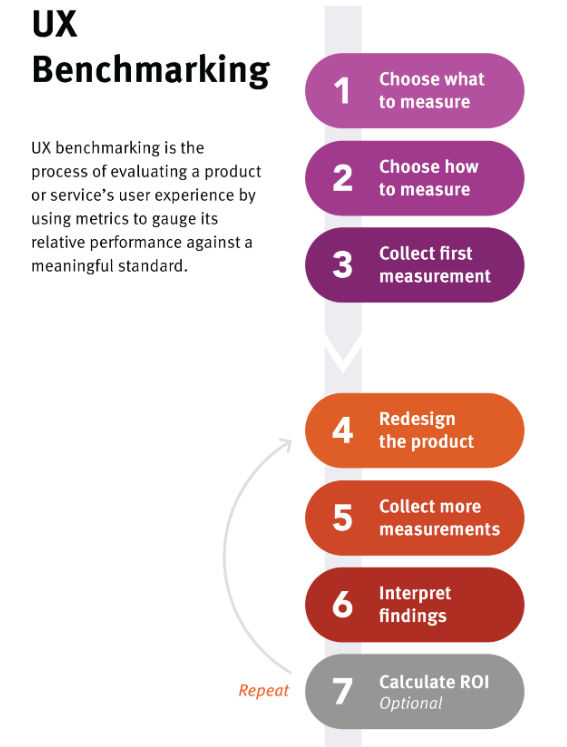
Benchmarking
-
Benchmarking studies measure the baseline.
-
It also helps to track how the design and functional changes impact the user experience.
-
Two main ways to benchmark -
- Stand-alone benchmarking ~ Also known as Usability benchmarking, it helps to establish the starting point to track how the user experience is impacted by your design iterations.
- Competitive analysis ~ It helps generate ideas. Assessing multiple websites gives you insights on what works and what doesn’t, to make sound design decisions.
Expert Review
- Expert reviews are valuable for identifying usability problems and potential areas for improvement in a product’s design.
- They are particularly useful when conducted early in the design process to catch issues before they become costly to fix.
- However, it’s important to complement expert reviews with other user research methods, such as usability testing, to gather insights from actual users.
- An expert review, also known as a usability inspection or heuristic evaluation, is a user research method used to assess the usability and user-friendliness of a product or interface.
Global and Cross-Cultural Research Techniques
- Global and cross-cultural research techniques are methods and approaches used in user research to study user behavior, preferences, and needs across different cultural contexts and regions.
- Conducting research in diverse cultural settings is essential for creating products and services that are inclusive and effective for a global audience.
- They help identify cultural nuances, user expectations, and usability issues that may vary across different regions and cultures, ultimately leading to more inclusive and effective user experiences.
Power Distance (PDI)
- According to Geert Hofstede, Power Distance Index (PDI) measures the extent to which the less powerful members of organizations and institutions (like the family) accept and expect that power is distributed unequally.
- It suggests the degree of society’s level of inequality endorsed by the followers as much as by the leaders.
- Understanding and acknowledging the influence of Power Distance in user research is essential for conducting respectful and effective research in cross-cultural contexts.
- Researchers should strive to create an inclusive and culturally sensitive research environment that allows participants to share their perspectives and experiences authentically.
Individualism VS Collectivist
- People from societies with a high score on individualism are those who take the initiative to act on their needs and desires and make their own decisions.
- They visit your site out of interest, to realize their own goals and make their own decisions.
- One needs to focus on these individual requirements to convert them into loyal customers.
- On the other hand, people who belong to a collectivist culture consider the interest of the group first, rather than their own interest.
- Consider this on your web portal and offer enough reference points, such as testimonials, ‘popular’ categories, or social media sharing options to gather feedback from peers.
Uncertainty Avoidance (UAI)
- Understanding Uncertainty Avoidance can help researchers adapt their methodologies, communication styles, and research processes to create a comfortable and productive environment for participants in different cultural contexts.
- It’s important to recognize that cultural dimensions like UAI can significantly impact user research outcomes and should be considered when planning and conducting research in cross-cultural settings.
- It measures the extent to which members of a society feel uncomfortable with ambiguity, uncertainty, and unstructured situations.
- It reflects a culture’s willingness to accept risks and its preference for rules, procedures, and formal systems to mitigate uncertainty.
- In the context of user research, understanding Uncertainty Avoidance can be valuable when conducting research in different cultural settings.
Long-Term versus Short-Term Orientation (LTO)
-
People with short-term orientation focus more on the past and present than on the future. They prefer quick results that are in line with known values and traditions.
-
People with long-term orientation make accurate decisions for the future. These users have to be offered detailed information and advantages that truly convince them of your product’s value.
Some Other Research Methods
Task Analysis
- Task analysis is a user research method used to systematically study and document the steps, actions, and processes that individuals perform to complete a specific task or achieve a particular goal.
- It is a valuable technique for understanding how users interact with a product, system, or interface, and it can provide insights for improving usability, efficiency, and user experience.
- Task analysis is a usability research because it provides a detailed understanding of user behavior and helps designers and developers create products and interfaces that align with users’ needs and goals.
- It is particularly useful in designing intuitive interfaces and optimizing complex workflows.
Surveys and Questionnaires
- These are quantitative modes of research and offers a quick way to collect information from a large number of users.
- The obvious limitation here is lack of any interaction between the researcher and the users.
Card Sorts
- Card sorting is a user research method commonly used in information architecture and usability testing to understand how users organize and categorize information.
- It helps designers and researchers determine the most intuitive and user-friendly way to structure content and navigation within a website, application, or other information system.
- Card sorting is a valuable technique for improving the user experience by ensuring that information is organized in a way that aligns with how users naturally think and categorize.
- It provides empirical data to inform information architecture decisions and helps designers create more user-centric systems.

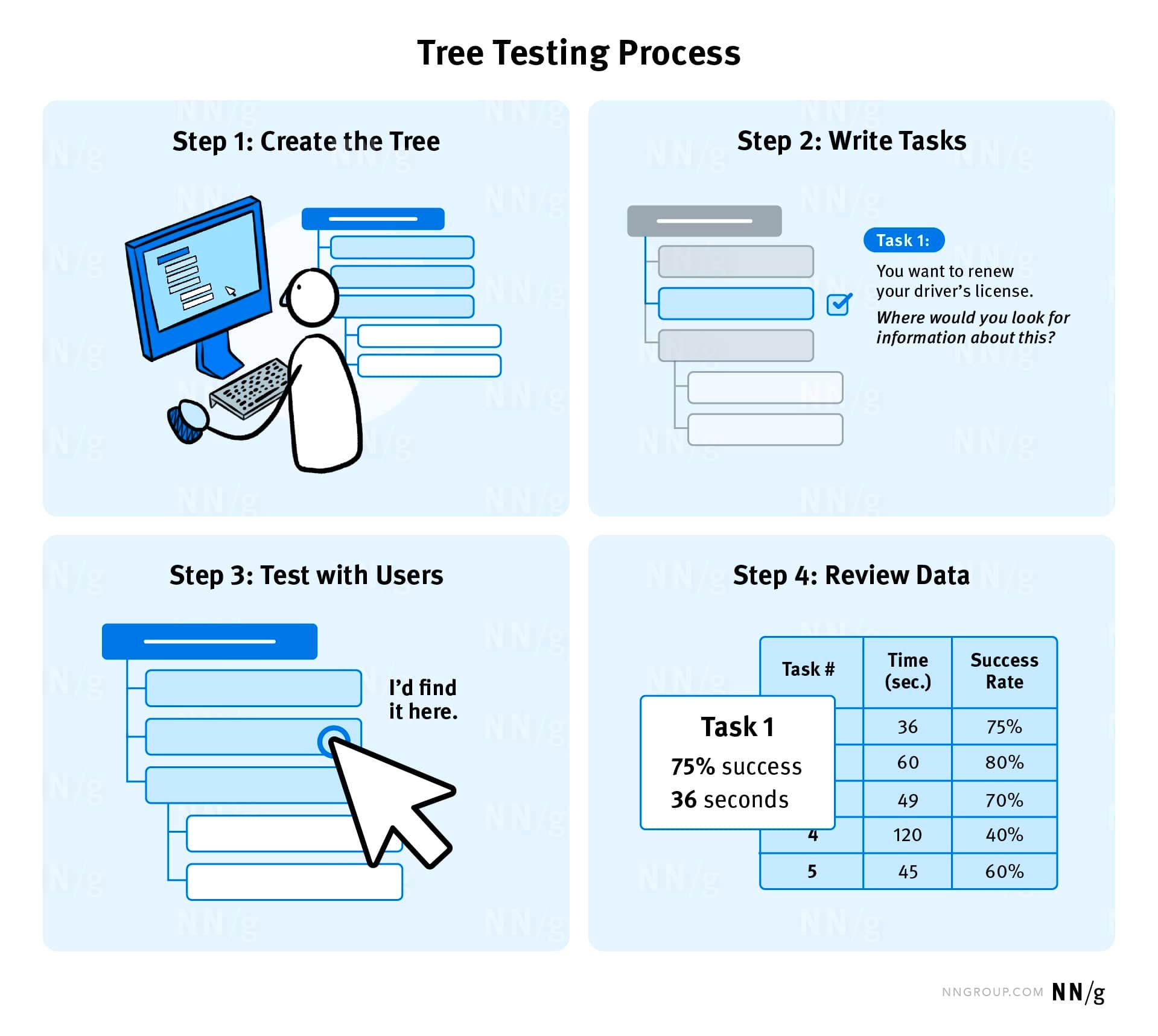
Tree Test
- Tree testing is a user research method used to evaluate the effectiveness and findability of a website’s information architecture and navigation structure.
- It helps identify how easily users can locate specific content or tasks within a website’s hierarchy.
- Tree testing is typically performed using a text-based representation of a website’s structure, without the influence of visual design or distractions.
- Tree testing is a valuable method for optimizing a website’s navigation and information architecture, ensuring that users can easily find the content or complete the tasks they need.
- It provides data-driven insights to inform design decisions and enhance the overall user experience.
A/B Tests
- A/B testing, also known as split testing, compares two versions of a web page to see which one performs better.
- It focuses on providing similar users with two or more options and documenting the user’s preferences amongst the options.
- There are also focused A/B tests on specific aspects of the product such as the design elements, information hierarchy, navigation and so on.
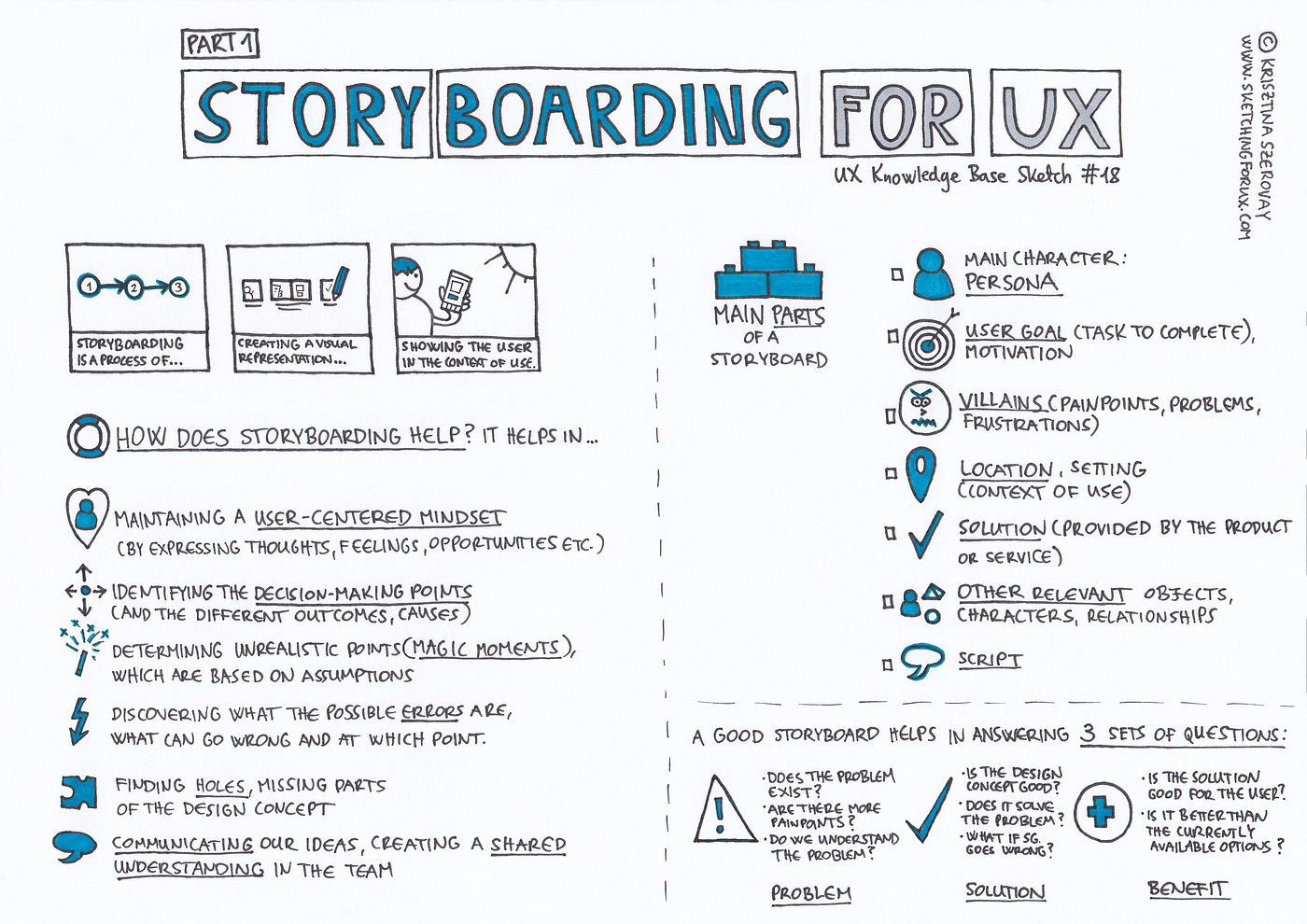
Storyboard
- Storyboarding is a user research method used to visually represent user experiences and interactions with a product, service, or system.
- It is a valuable technique for capturing and communicating user stories, scenarios, or use cases in a structured and visual format.
- Storyboarding helps researchers and designers understand user needs, identify pain points, and envision potential solutions.
User Persona
- User personas are valuable tools that help ensure your product or service remains user-centered throughout the development process.
- They provide a shared understanding of your users and help align the team’s efforts toward meeting their needs and delivering a more satisfying user experience.
- They are fictional representations of your target users, created based on real user data and research findings.
- User personas help design and development teams better understand and empathize with their users’ needs, goals, behaviors, and pain points.
Reporting on User Research
Reporting on user research is a critical step in the user-centered design process. Effective reporting ensures that the insights and findings from your research are communicated clearly and are actionable for the design and development teams. There are various types of deliverables—from no deliverable at all to a full report. It is highly advisable that to choose a deliverable that allows to share the research findings and recommendations in the available time frame and considers the needs of the audience.
No Deliverable ~
- If one involves the right people throughout the research, one may just need to have a discussion on the findings and make changes to the design without spending any time creating a deliverable.
- However, it is required to keep in mind that one will have no record of your findings for later use.
Quick Findings ~
- If time is a constraint, the deliverable can be in the form of an email or a document which describes the overall findings and proposed design changes.
Detailed Reports ~
- A report gives the freedom to describe the findings and recommendations comprehensively and in as much detail as needed. Reports have value as proof of the research.
Presentations ~
- When the deliverable is a presentation, one needs to optimize it for effective delivery. Those who view it later should be able to understand it easily, without the explanations one needs to initially give during your presentation.
Findings and Recommendations Matrix ~
- Gathers all recommendations together. This is usually in a simple tabular format, summarizing the findings that led to each recommendation and if applicable, a severity rating for each issue.
Final Summary
Congrats!! You have completed the course. Hope you found it useful. Some of the key takeaways from this course are:
- User Research techniques with users
- User Research techniques without users
- Cultural factors to consider while designing an interface
- Qualitative techniques used for User Research
- Reporting User Research Findings