Table of contents
Open Table of contents
- User Experience and its meaning
- Form Follows Function Principal
- Why Good User Experience Ensures Better Business
- The Five Planes of User Experience Design
- Strategy Plane
- User Segmentation Technique
- Usability and User Research Techniques
- Creating Personas for User Needs
- What is Strategy Document
- Scope Plane
- Structure Plane
- Interaction Design - Error Handling
- Information Architectural Approaches
- Skeleton Plane
- Exploring different Navigation Types
- Types of Information Design
- Surface Plane
- Explaining the Senses
- Final Take-away
User Experience and its meaning
- User Experience (UX) refers to the overall experience that a person/user has when interacting with a product, system, or service.
- It encompasses a wide range of factors which influence a user’s perception and satisfaction with their interaction, including their emotions, preferences, and perceptions.
- UX design aims to create products and services that are user-centered and provide a positive, meaningful, and efficient experience for the user.
- A well-designed product looks pleasant to the eye and feels good to touch.
- It is a multidisciplinary field that involves collaboration between designers, researchers, developers, and other professionals to achieve these goals.
Form Follows Function Principal
"Form follows function" is a design principle that suggests the shape and appearance of an object or structure should be primarily determined by its intended function or purpose.
This principle is closely associated with modernist design movements, particularly in architecture and industrial design, and it has had a significant influence on various fields of design.- This “form follows function” is a guiding principle in many design disciplines, it’s essential to note that not all design adheres strictly to this principle.
- There are instances where designers intentionally incorporate decorative or ornamental elements into their work, even if they may not directly relate to the primary function.
- These elements can add cultural, artistic, or symbolic value to a design.
- Ultimately, the balance between form and function may vary depending on the context and goals of a particular design project.
Lets clear the air about Aesthetic, Functional and UX Design
-
Aesthetic design makes sure that the button has an attractive shape and texture.
-
Functional design ensures that it sets off the suitable action on the device.
-
User experience (UX) design ensures that the functional and aesthetic features of the button work in connection with the rest of the product.
Why Good User Experience Ensures Better Business
A good user experience (UX) can have a significant impact on a business’s success. A positive and well-crafted user experience can lead to several benefits that contribute to the overall success and growth of a business. Here are some reasons why good UX ensures better business outcomes:
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Good UX design ensures that customers can easily and effectively use the products or services. When users have a satisfying experience, they are more likely to be happy with the brand, recommend it to others, and become loyal customers.
- Customer Loyalty: A positive UX encourages customer loyalty. Users are more likely to stick with a brand or product that consistently meets their needs and provides a pleasant experience. This loyalty can lead to long-term customer relationships and repeat business.
- Reduced Churn: Churn refers to the rate at which customers stop using a product or service. Good UX can help reduce churn by addressing pain points and frustrations that might otherwise drive customers away.
- Cost Savings: Good UX can reduce support and maintenance costs. When users encounter fewer issues and have a better understanding of how to use the product or service, there are fewer customer support inquiries and less need for ongoing updates to fix usability issues.
- Better SEO Ranking: Search engines like Google consider user experience as a ranking factor. Websites and applications that offer a good UX, with fast load times and mobile-friendly designs, are more likely to rank higher in search results, attracting more organic traffic.
- User-Centered Innovation: Listening to user feedback and incorporating it into the design process can lead to innovative improvements in the products or services. By aligning the offerings with user needs and preferences, one can stay relevant and ahead of the curve.
Important Notes on Minding the Users
- The practice of designing a product or service keeping users in mind is called User-centered Design (UCD).
- The concept of UCD is very simple and takes the user into account during every step of the design process. A UCD process ensures that compromises don’t happen by accident.
The Five Planes of User Experience Design
- The “Five Planes of User Experience Design” is a framework that helps designers and UX professionals think comprehensively about the various aspects and dimensions of user experience.
- This framework breaks down the user experience into five interconnected planes or layers, each of which represents a different facet of the overall experience.
- These planes provide a structured approach to understanding, designing, and evaluating user experiences.
The five planes are as follows:
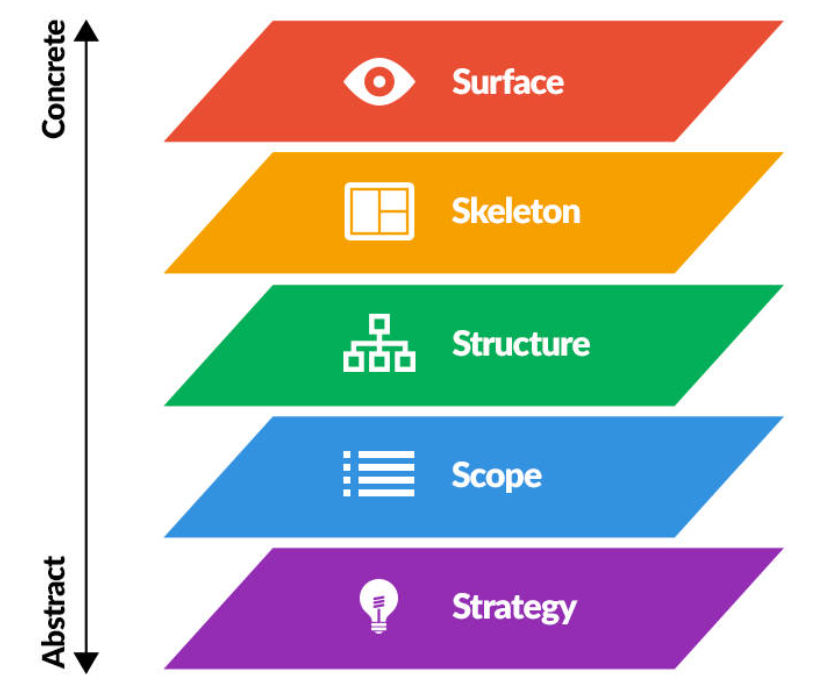
Strategy Plane ~
- This plane is the highest-level and focuses on the overarching goals and objectives of the project.
- It addresses questions like: What are we trying to achieve? Who are our target users? What are their needs and pain points? What are the business goals?
- Key activities at this level include market research, user research, defining user personas, setting project objectives, and establishing a clear vision and strategy for the user experience.
Scope Plane ~
- The scope plane defines the features, functionalities, and content that will be included in the project.
- It involves determining what the product or service will offer and what it won’t.
- Key activities in this plane include creating user stories, feature prioritization, content strategy, and defining the boundaries of the project.
Structure Plane ~
- This plane deals with how information and content are organized and structured within the product or service.
- It encompasses information architecture, navigation, and the overall layout.
- Key activities include creating site maps, wireframes, and prototypes to design the layout and navigation flow.
Skeleton Plane ~
- The skeleton plane focuses on the visual and interactive aspects of the user interface.
- It addresses the design of individual screens or pages, including the placement of elements, typography, color schemes, and interactive components.
- Key activities here involve creating detailed interface designs, visual style guides, and interactive prototypes to give the design a tangible form.
Surface Plane ~
- The surface plane is the final layer, concerned with the aesthetics and presentation of the user interface.
- It deals with the sensory aspects that users perceive, such as graphics, animations, and overall visual appeal.
- Key activities in this plane include applying visual design principles, choosing imagery, refining the user interface, and ensuring consistency in the visual presentation.
These five planes are interconnected and should be considered holistically throughout the design process. Changes made in one plane may have implications for the others, so designers need to carefully balance and align them to create a cohesive and effective user experience.
Strategy Plane
- In the context of the “Five Planes of User Experience Design,” the “Strategy Plane” is the topmost layer and represents the strategic foundation of the UX design process.
- This plane focuses on defining the high-level goals, objectives, and guiding principles that will shape the entire user experience.
- An effective UX strategy ensures that the resulting product or service not only meets user expectations but also contributes to the overall success of the project.

Product Objectives -
- Product objectives should not exist as an unspoken understanding within the team members, or else different people in the project will have different ideas about it.
- In the Strategy Plane of UX design, defining clear and well-defined product objectives is a critical step.
- Product objectives are specific, measurable goals that guide the design and development of a product or service. These objectives help align the user experience (UX) design process with the overall strategic direction of the project.
To define a product objective, we need to consider the following factors.
1. Business Goals ->
- Business goals help a business grow and achieve its objectives.
- The aim is to identify how the product will help to realize the objectives of the organization.
2. Brand Identity ->
- The concept of brand identity is not just visual but a set of conceptual associations or emotional reactions.
- An impression of the organization is created in the mind of the user who interacts with the product.
3. Success Metrics ->
- Success metrics are the indicators that we can track after the product has been launched to see if it meets the product objectives and user needs.
- It also gives an insight how effectively the user experience is meeting strategic goals.User Needs -
- User needs play a central role in the Strategy Plane of UX (User Experience) design.
- Understanding and addressing user needs is crucial for creating a product or service that meets the expectations and requirements of the target audience.
- It involves understanding, prioritizing, and addressing user needs as the driving force behind the project’s objectives and design decisions.
- By placing user needs at the forefront of the strategy, designers are more likely to create products and services that resonate with their target audience and ultimately lead to a successful user experience.
Techniques to Understand User Needs
1. User Segmentation
2. Usability and User Research
3. Creating PersonasUser Segmentation Technique
User segmentation is a technique in UX (User Experience) design and marketing that involves dividing a target audience or user base into distinct groups or segments based on shared characteristics, behaviors, or demographics. The goal of user segmentation is to better understand the diverse needs, preferences, and behaviors of different user groups, allowing designers and marketers to tailor their products, services, and messaging to each segment more effectively.
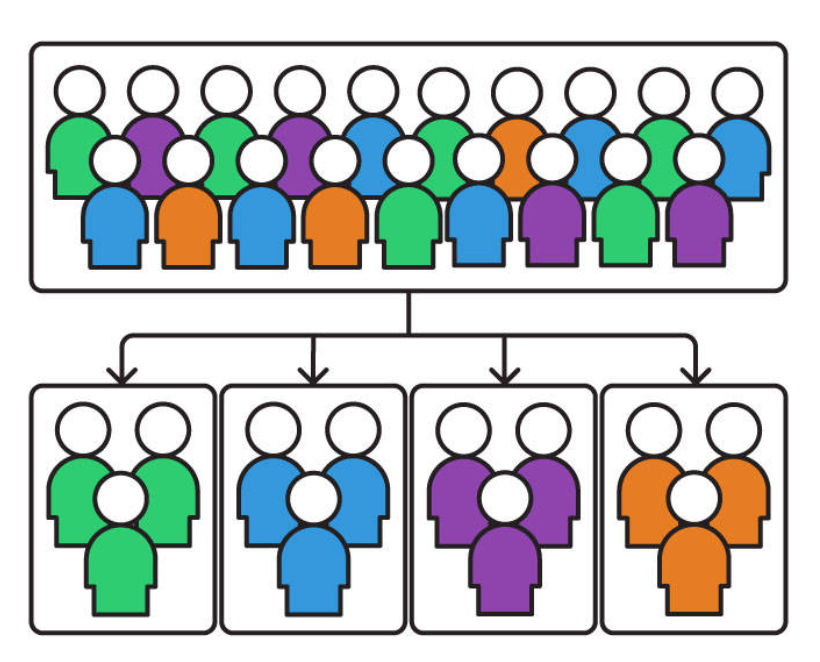
Here are some common techniques and strategies for user segmentation:
Demographic Segmentation:
- This involves dividing users based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, education, marital status, and geographic location. Demographic data can provide valuable insights into user preferences and behaviors.
Psychographic Segmentation:
- Psychographic segmentation focuses on users’ psychological and lifestyle characteristics. This can include factors such as personality traits, values, interests, hobbies, opinions, and attitudes. Psychographic segmentation helps create a more nuanced understanding of users.
Behavioral Segmentation:
- Behavioral segmentation categorizes users based on their behaviors and actions. It considers factors like product usage frequency, purchase history, website interactions, and engagement levels. Behavioral data is often collected through analytics tools.
Usability and User Research Techniques
Usability and user research techniques are essential components of user-centered design and product development processes. They help designers and teams understand user needs, behaviors, and preferences, leading to the creation of more user-friendly and effective products.
User Research:
- It deals with collecting the user data needed to develop the knowledge about the user by means of research tools.
Surveys, interviews or focus group study:
- It help us to gather information about general attitudes and perceptions of users.
User tests or field studies:
- It help us to understand a specific aspect of user behavior and interaction with the product.
Market research method:
- Like surveys and focus groups can be valuable sources of general information about the users.
Contextual inquiry:
- Helps us to understand users in the context of their everyday lives.
Task analysis:
- Helps us analyze the precise steps user do to complete a task.
User testing:
- It is getting the users to test what you have produced.
Card sorting:
- It is a method used to understand how users categorize information.
Creating Personas for User Needs
Creating personas is a valuable technique in UX (User Experience) design for understanding and empathizing with different user needs, behaviors, and preferences.
Personas are fictional representations of typical users, and they help designers and teams make informed design decisions that align with user expectations. By creating and using personas, one can ensure that the design and development efforts are focused on meeting the needs of real users, leading to more user-centered and successful products and services.
What is Strategy Document
A formal strategy document is created listing product objectives and user needs. The document provides an analysis of objectives and how they fit into the organization.
- Keep the strategy document precise.
- The document must be shared with all members of the team.
Scope Plane
- The Scope Plane is a critical step in the UX design process because it sets the stage for the subsequent phases of research, design, testing, and implementation.
- It helps avoid scope creep, where the project expands beyond its original boundaries, which can lead to delays, budget overruns, and a diminished user experience.
- By defining and documenting the scope upfront, the design team can work more efficiently and effectively to achieve the project’s objectives.
- This phase is important for establishing what the project will encompass and what it won’t. It helps align the design team, stakeholders, and other project members on the project’s objectives and deliverables.
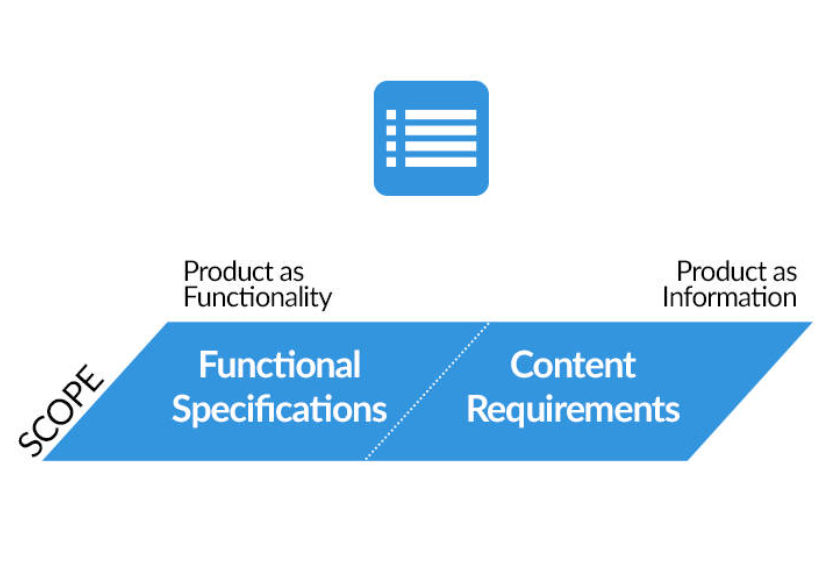
Functionality and Content ~
- Functional specifications mainly define the scope of the project.
- The functionality side deals with the feature set and the information side deals with the content of the product.
Common Terms to explore -
- Explaining Requirements -> Defining requirements intends to find ways to remove the blocks. Some requirements apply only to a specific feature, and some apply to the product as a whole. The most productive source of requirements are the users.
- Prioritizing Requirements -> Everyone will have at least one idea for a feature that could be added to the product. We need to prioritize the features that must be included in the scope of the project.
- Understanding Scenarios -> To determine the requirements, we shall put our personas into little stories called scenarios. A scenario is a short, simple narrative that shows how a persona might fulfill one of those user needs. We shall also do a competitor analysis if anyone else in the same business is trying to meet similar user needs and product objectives.
Functional Specifications -
In UX (User Experience) design and development, a Functional Specification (often referred to as a “Functional Spec” or “Functional Requirements Document”) is a comprehensive document that outlines the detailed functionality and behavior of a product or system. It serves as a critical bridge between the design and development phases by specifying what the product should do, how it should behave, and how users should interact with it.
General rules apply while writing the functional specifications.
1. Be positive.
2. Be specific.
3. Avoid subjective language.Content Requirements -
Content requirements are a vital component of UX (User Experience) design and are critical for ensuring that the content within a product, website, or application meets user needs and supports the overall user experience. Content encompasses text, images, videos, audio, and any other media or information presented to users. Effective content requirements ensure that the content within a product is user-centric, informative, engaging, and aligned with the overall UX design. They also contribute to a cohesive and consistent user experience that meets the needs and expectations of the target audience.
Structure Plane
- In UX (User Experience) design, the “Structure Plane” refers to one of the five planes of user experience, which provide a framework for understanding and designing the user experience of a product or service.
- The Structure Plane specifically focuses on the organization and arrangement of information and functionality within a digital product, such as a website or application.
- It involves creating a clear and logical structure that enables users to find information, navigate through the product, and complete tasks efficiently.
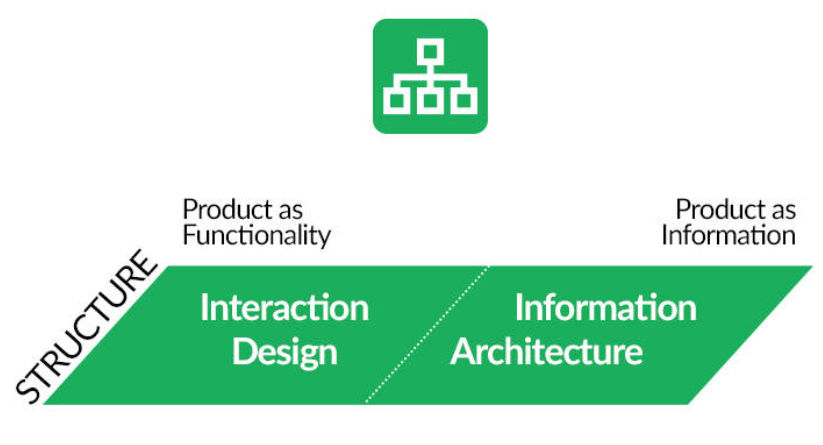
This mainly involves two disciplines.
1. Interaction Design
2. Information ArchitectureInteraction Design -
Interaction design (IxD) is a multidisciplinary field within user experience (UX) design that focuses on creating meaningful and intuitive interactions between users and digital products, such as websites, mobile apps, software applications, and other interactive systems. Interaction designers work to ensure that users can easily and effectively accomplish their goals while using these products. It mainly describes the possible user behavior. It defines how the system will accommodate and respond to that behavior.
Notes on Conceptual Model
Conceptual models are defined as the user’s reactions of how the created interactive elements will behave. Understanding the conceptual model lets take consistent design decisions. Users are accustomed to conceptual models, due to which users find it easy to adapt.
Information Architecture -
Information Architecture (IA) is a foundational concept in the field of User Experience (UX) design and web development. It refers to the structural organization and arrangement of information within a digital product, such as a website, mobile app, or software application. IA focuses on creating a logical, user-centric, and efficient information structure that enables users to find and interact with content or functionality effectively. It is mainly concerned with how people cognitively process information. A visual representation of the structure is the most efficient way to communicate branches, groups, and interrelationships among the components of our product.
Interaction Design - Error Handling
Error handling is a crucial aspect of interaction design, as it directly impacts the user experience when things go wrong. Effective error handling strategies help users understand, recover from, and prevent errors while using digital products. Error handling deals with the mistakes user might make, how the system will respond to it and what can the system do to prevent those mistakes. A user-friendly and empathetic approach to error handling can enhance user trust and satisfaction.
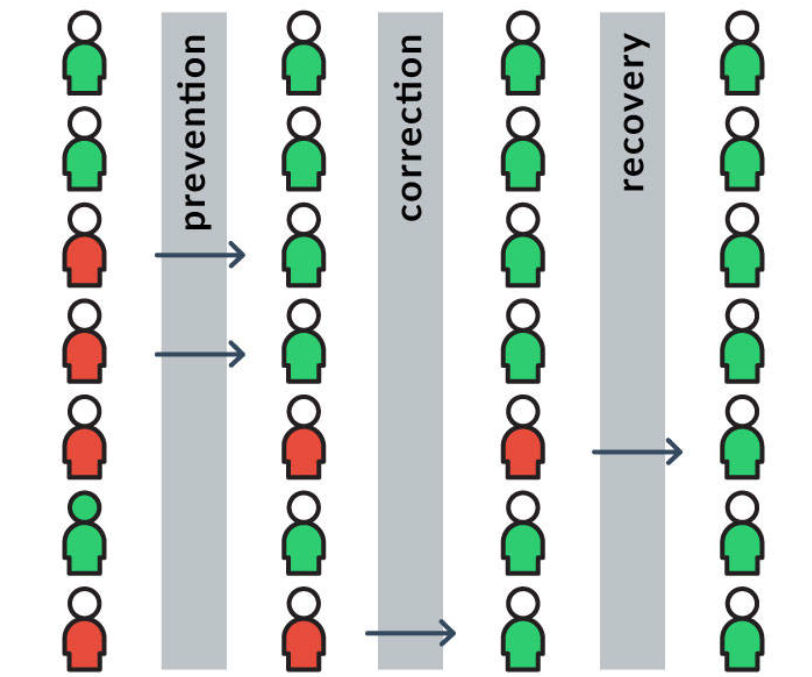
There are three layers of error handling.
-
Error Prevention:
- The best way to handle errors is to prevent them from occurring in the first place.
- Design systems and interfaces that guide users to make correct choices and take appropriate actions.
- Use clear and concise labels, instructions, and feedback to minimize the likelihood of user errors.
- Implement validation checks to catch and address errors in real-time, such as verifying the format of user inputs in forms.
-
Error Correction:
- Error correction is a fundamental aspect of interaction design and user experience (UX) that involves guiding users to recognize and rectify errors or mistakes they may make while interacting with digital products or systems.
- Effective error correction strategies are essential for maintaining a smooth and frustration-free user experience.
-
Error Recovery:
- Provide clear guidance on how users can correct errors and continue with their tasks. Suggest specific actions, if applicable.
- Offer undo options or the ability to revert changes in case users make unintended actions.
Information Architectural Approaches
If we follow an adaptable architecture, it will be easy to add content at any point of the project. The basic unit of information is called a node, and it can correspond to any piece or group of information.
The nodes can be arranged in different ways.
1. Hierarchical ->
- A hierarchical structure refers to the organization of content or information in a way that represents a clear and structured hierarchy or tree-like relationship.
- This structure is essential for helping users navigate through a digital product, such as a website or app, by providing a logical and intuitive path to access information or features.
2. Matrix ->
- A matrix structure refers to an organizational approach for structuring and categorizing information or content that doesn't fit neatly into a single hierarchical hierarchy.
- Instead of using a traditional top-down hierarchy, a matrix structure allows for content to be organized along multiple dimensions or attributes.
- This approach is particularly useful when dealing with complex or multifaceted information.
3. Organic ->
- An "organic structure" in the context of Information Architecture (IA) within User Experience (UX) design refers to a non-hierarchical or loosely structured way of organizing information or content.
- It contrasts with traditional hierarchical structures that use clear top-down categorization.
- Instead, an organic structure embraces flexibility and often mimics the way users naturally think or navigate when searching for information.
4. Sequential ->
- A sequential structure in Information Architecture (IA) within User Experience (UX) design refers to an organizational approach that arranges content or tasks in a linear or step-by-step fashion.
- This structure guides users through a predefined sequence of actions or content, often with a clear beginning and end.
- Sequential structures are commonly used in processes where a specific order or flow is essential.Extra Notes
Organizing Principles
-
In an information structure, the nodes are arranged according to organizing principles. It is the criteria by which the nodes are separated and grouped.
-
The organizing principles applied across different levels of the product could be different. Organizing principles are closely tied to the user needs and product objectives.
Language and Metadata
-
The language used in the product is as important as structure. The users will not be able to find their way around the architecture if they can’t understand the nomenclature. The best way to understand how users communicate is to talk to them during the research phase.
-
Metadata means information about information. A system that includes metadata should have a controlled vocabulary or thesaurus.
Skeleton Plane
- In the context of User Experience (UX) design and the five planes of UX design, the “Skeleton Plane” refers to the stage in the design process where the basic structure and layout of a digital product are created.
- It serves as an intermediate step between the “Structure Plane” (which defines the organization and hierarchy of content) and the “Surface Plane” (which deals with the visual design and aesthetics of the product).
- The Skeleton Plane focuses on defining the functional elements, interactions, and navigation of the user interface.
- Once the skeleton is refined and validated, designers can proceed to the Surface Plane to apply the visual design, colors, typography, and other aesthetic elements to complete the user interface.
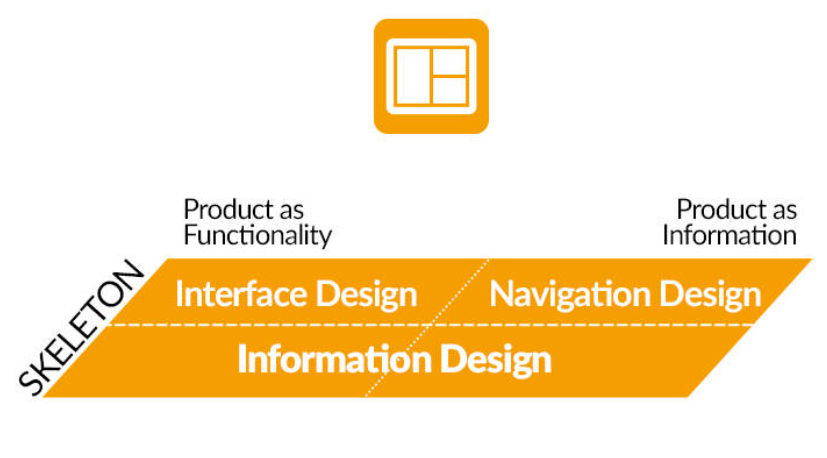
It consists of the following elements.
1. Interface Design
2. Navigation Design
3. Information DesignInterface Design
Designing the correct interface elements for the tasks that the user is trying to perform and arranging them in a way that will be readily understood and can be easily used, is called Interface Design. A good interface must allow the users to notice the important stuff and it should recognize the action that users are most likely to perform.
Navigation Design
A good navigation design must fulfill three simultaneous goals. It should allow the users to get from one point to the other easily. It should communicate the relationship between its elements. It should communicate the relationship between its contents and the current screen that the user is viewing.
Navigation Types
A good product should provide multiple navigation systems that will enable the user to navigate the product easily. These are some common type of navigation systems.
- Global Navigation
- Local Navigation
- Supplementary Navigation
- Contextual Navigation
- Courtesy Navigation
Information Design
Information design deals with presenting information in a way that people understand it effectively and efficiently. It can be a visual decision like choosing the type of graph or icons that would work better for the users. It also deals with grouping and arranging pieces of information.
Exploring different Navigation Types
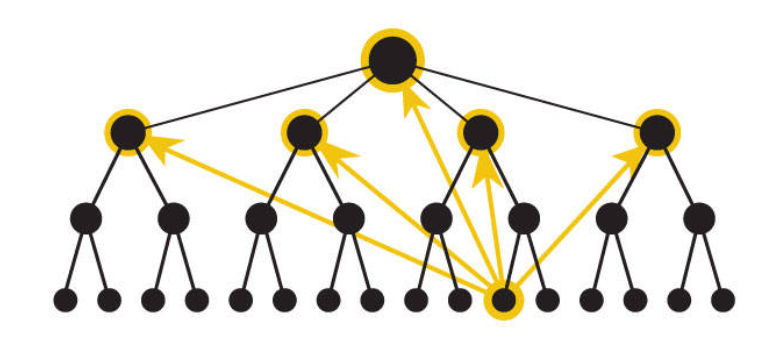
- Global Navigation ~
- Global navigation in UX (User Experience) design refers to the primary and consistent method for users to navigate through a digital product, typically found at the top or side of a website or application interface.
- Global navigation is a critical element in UX design, as it directly impacts how users move through a digital product.
- It serves as the main menu or navigation system that provides access to the most important sections and features of the product, regardless of the user’s current location within the application.
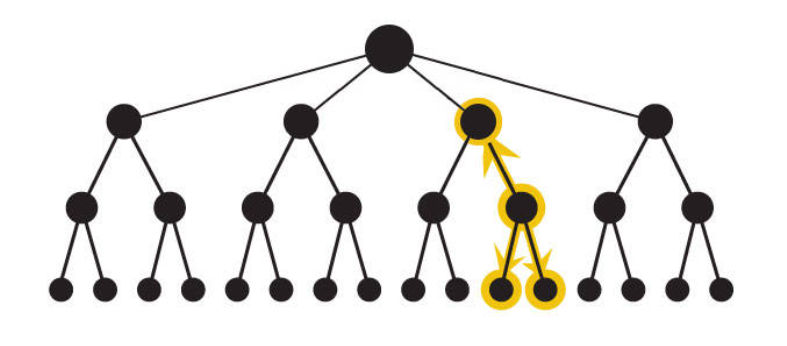
- Local Navigation ~
- Local navigation plays a crucial role in guiding users through the content and features of a digital product.
- It helps users efficiently explore and engage with information within a specific context, contributing to an improved overall user experience.
- Local navigation is context-specific and focuses on helping users navigate within a particular area or topic.
- Supplementary Navigation ~
- Supplementary navigation elements should be designed with a clear purpose and user-centric approach.
- They should enhance the user experience by providing convenient access to relevant content or functionality without overwhelming users with options.
- It’s important to strike a balance between offering supplementary navigation and maintaining a clean and uncluttered user interface.
- Usability testing and user feedback are valuable for ensuring that supplementary navigation elements meet users’ needs effectively.
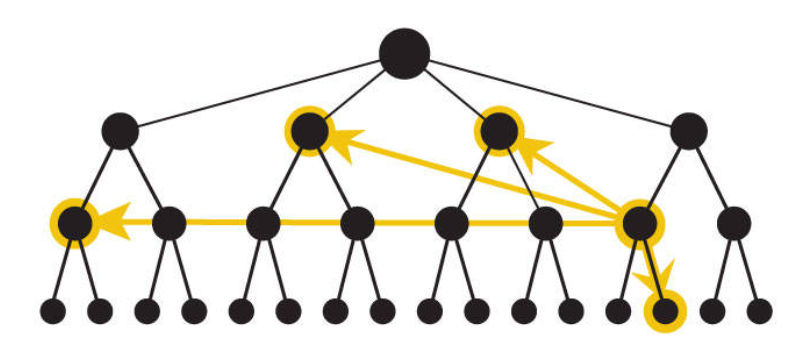
- Contextual Navigation ~
- Contextual navigation is a valuable UX design strategy because it empowers users with options and guidance that are tailored to their current context, reducing the cognitive load and streamlining their interactions with the product.
- It contributes to a more intuitive and user-friendly experience by anticipating and addressing user needs in real-time.
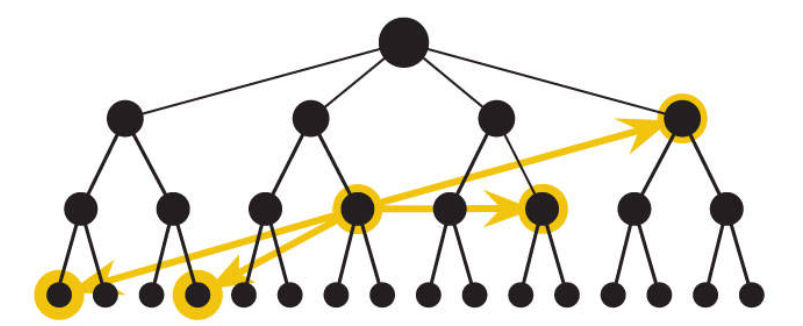
- Courtesy Navigation ~
- Courtesy navigation in UX (User Experience) design refers to a set of navigation elements or features that are offered to users as a gesture of assistance or convenience, often without being directly related to the primary goals or tasks of a digital product.
- These navigation options are provided to enhance the overall user experience and demonstrate consideration for users’ needs.
- Courtesy navigation aims to make it easier for users to explore, access additional resources, or perform secondary actions within a product.
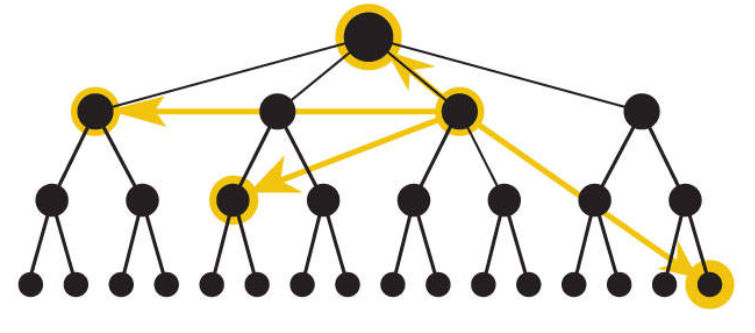
Types of Information Design
Wayfinding -> helps the user to know where they are and where they can go. The idea comes from public spaces design in the real world. This involves both information design and navigation design.
Wireframe -> A wireframe is a schematic representation of all the components of a screen and how they fit together. It mainly shows a detailed layout where information design, interface design, and navigation design come together. Each screen in the wireframe is annotated by the designer. Creating a wireframe helps us to tackle the skeleton issues first.
Surface Plane
- The Surface Plane in UX (User Experience) design refers to the final layer of the five planes of user experience design.
- It focuses on the visual and sensory aspects of a digital product, including its aesthetics, presentation, and overall look and feel.
- The Surface Plane is where designers apply the principles of visual design to create an appealing and cohesive user interface (UI).
- The surface plane is also called the sensory design layer which blends content, functionality, and aesthetics to produce a design that pleases senses of the user.
Sensory Design
Sensory design in UX (User Experience) design refers to the intentional consideration and integration of sensory experiences—beyond visual and auditory—in the design of digital products and interfaces. While traditional UX design often focuses on visual and auditory elements, sensory design broadens the scope to include touch, haptic feedback, and even smell and taste in certain contexts. The goal of sensory design is to create immersive and engaging experiences that resonate with users on a deeper level.
Making Sense of the Senses: The experience users have with the product or service comes through their senses.
Vision
Hearing
Touch
Smell
TasteExplaining the Senses
Follow the Eye ~ The visual design of a product can be evaluated using eye-tracking. It analyzes how the user’s eyes move around the screen. A good visual design should draw the user’s attention towards something important to the strategic product objectives.
Contrast ~ A visual design without contrast will cause user’s eye to move around the screen without focusing anything in particular. A good contrast helps the user to communicate conceptual groups in information design.
Uniformity ~ Maintaining the same size for all similar components in the product and following a grid-based layout effectively ensures a uniformity in the design, and it communicates effectively without confusing the users.
Color Palettes ~ The usage of proper color is essential to communicate a brand identity. The colors from the brand’s color palette should be chosen in such a way they work together, complementing each other without competing.
Typography ~ The usage of typeface or fonts is also an essential part of a brand’s visual style. Simple typefaces are always better than ornate typefaces as its easy for users to read. Always use a few typefaces together to achieve better results. Use different styles only when one have to communicate differences in the information.
Design comp (Design Composite) ~ is the visualization of the finished product. It doesn’t have to match the wireframe precisely, but there should be a one-to-one correlation between the components in both.
Style guide ~ is the definitive documentation of the design decisions. It defines all the aspects of design such as design grids, color palettes, typography standards etc. Creating a style guide helps in imposing design consistency across an organization.
Roles ~ To create a successful user experience, one should have someone in the organization think about each of the five planes – strategy, scope, structure, skeleton, and surface.
Final Take-away
To create a successful User Experience, One should take care of the following five planes.
- The Strategy Plane: Product Objectives and User Needs
- The Scope Plane: Functional Specifications and Content Requirements
- The Structure Plane: Interaction Design and Information Architecture
- The Skeleton Plane: Interface Design, Navigation Design,and Information Design
- The Surface Plane: Sensory Design